Understanding Triceps Tendonitis: Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment for Elbow Pain
Triceps Tendonitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Triceps tendonitis is a painful condition caused by overuse or injury of the triceps tendon in the elbow. This tendon attaches the triceps muscle in the upper arm to the elbow. Triceps tendonitis causes pain, swelling, and weakness in the back of the elbow that can make it difficult to straighten the arm.
If you have persistent elbow pain when using your triceps that doesn’t improve with rest, you may have triceps tendonitis. Read on to learn what causes triceps tendinitis, symptoms to watch for, and how it’s diagnosed and treated.
What is the Triceps Tendon?
The triceps is the large three-headed muscle on the back of your upper arm. It straightens your elbow so you can push, press, throw objects or swing a golf club or baseball bat.
The triceps muscle connects to the forearm bone called the olecranon via the triceps tendon. This tendon attaches the triceps muscle to the bony bump on the back of your elbow. It allows the triceps to straighten (extend) the arm at the elbow joint when contracted.
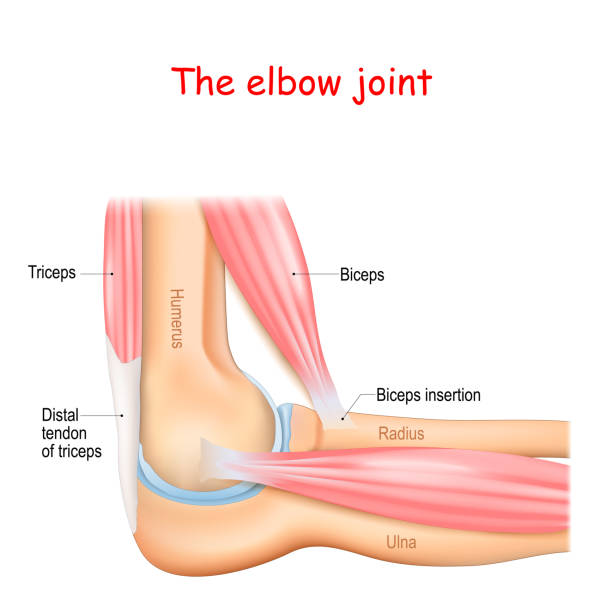
The triceps muscle contracts, pulling on the triceps tendon to straighten the elbow.
What is Triceps Tendonitis?
Triceps tendonitis is inflammation of the triceps tendon at the elbow joint. It causes pain and swelling where the tendon attaches near the tip of the elbow.
Triceps tendonitis is often caused by tiny tears or repeated strain to the tendon fibers from overuse. Sports, weightlifting, or jobs requiring repetitive arm motions can overwork the triceps tendon leading to irritation and microscopic damage.
As the tendon becomes inflamed, pain and weakness may make it difficult to straighten the elbow fully. Tiny calcific deposits can also form in the damaged tendon causing more irritation. If the tendon is overstressed with heavy use during the inflammatory phase, larger tears through the full thickness of the tendon can occur.

Common Causes and Risk Factors
There are several contributing factors and situations that can commonly lead to irritation of the triceps tendon:
- Repetitive elbow motion - Sports like weightlifting, swimming, baseball, tennis, and golf involve repetitive hard contraction of the triceps that can strain the tendon over time. Jobs requiring repetitive pushing, pressing, or overhead reaching can also overwork the tendon.
- Direct trauma - A sudden blow or injury directly over the triceps tendon can damage the tendon fibers leading to inflammation and weakness.
- Improper training - Weightlifters increasing the amount or intensity of triceps exercises too rapidly can overwhelm the tendon. Poor triceps training technique that strains the elbows can also contribute.
- Muscle imbalance - Weak or tight muscles in the shoulders and upper back can increase strain on the elbow tendons with triceps use.
- Bone spurs - Bone spurs that develop on the tip of the elbow may begin to rub and irritate the triceps tendon during elbow motion causing inflammation.

People are more prone to developing triceps tendonitis if they abruptly increase repetitive arm activities the triceps isn’t conditioned for or overload the triceps before it has fully healed from a previous strain or injury. Those with pre-existing elbow issues like arthritis are also at higher risk for triceps tendinitis.
Symptoms of Triceps Tendonitis
The most common symptoms of triceps tendonitis include:
- Pain in the back of the elbow - Aching or burning pain in the bony lump (olecranon process) near the tip of the elbow is the hallmark symptom. Pain usually worsens with any movement requiring triceps contraction like pushing, pressing down, or straightening the elbow.
- Swelling and bruising - The back of the elbow may look swollen and bruised. Pressing on the triceps tendon insertion can be quite painful.
- Stiffness and restricted mobility - Full extension (straightening) of the elbow becomes painful and difficult. Significant stiffness, tightness, and loss of motion may occur if the tendon is torn.
- Weak grip - Gripping objects can become weaker as triceps contraction exacerbates elbow pain.
- Tenderness - The back of the elbow is extremely tender to touch, especially on the bony tip of the elbow.
- Warmth and redness (severe cases) - If the triceps tendon becomes extensively inflamed, the back of the elbow may look red and feel warm to touch.
The degree of pain and disability depends on the severity of inflammation and damage to the actual tendon itself. Mild overuse irritation can cause subtle symptoms while larger partial or full tendon tears result in excruciating pain and significant loss of elbow function.
When to See a Doctor
It’s important to have your elbow examined by a sports medicine doctor or orthopedist if you have persistent triceps tendon pain that does not improve with a few days of rest. Chronic overuse can degenerate the tendon leading to larger tears or ruptures. Seeking early treatment helps optimize healing and reduce the risk of prolonged disability.
See a physician right away if you experience:
- Severe sudden elbow pain after an injury or fall on an outstretched arm
- Noticeable loss of elbow extension strength
- Intense pain at rest
- Persistent symptoms lasting over two weeks
- Significant elbow swelling, redness, warmth or bruising
- Numbness, tingling, or coldness in the forearm or hand
These can indicate a more serious elbow injury, tear, or compression of nerves that may require prompt evaluation and treatment.
Diagnosing Triceps Tendonitis
If triceps tendonitis is suspected, the physician will start by discussing your symptoms, daily activities, and elbow injury history. Details help determine potential causes of tendon irritation.
Diagnostic tests may include:
- Physical examination - The doctor will check range of motion, swelling, areas of tenderness, and elbow strength. They may have you flex and straighten your elbow against resistance to assess triceps function and reproduce pain.
- Imaging tests - X-rays can show bone spurs, calcium deposits, or loose bone fragments causing tendon irritation. MRI scans give detailed images of the triceps tendon to assess damage.
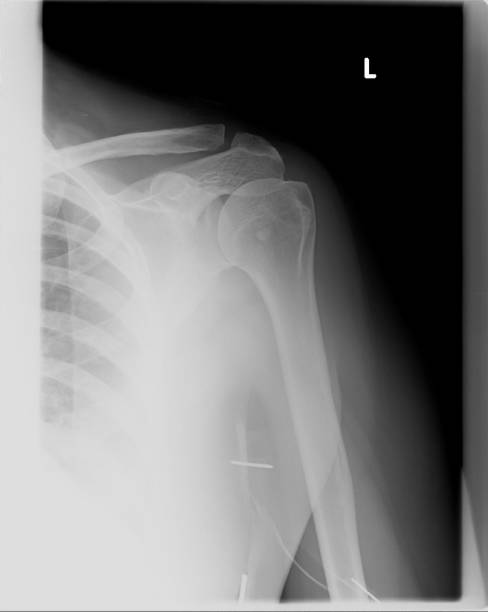
Based on the clinical evaluation, triceps tendonitis can often be accurately diagnosed. Imaging tests may be ordered if the doctor suspects a partial or complete tendon tear.
Treating Triceps Tendonitis
Treatment focuses on relieving pain and inflammation in the elbow while allowing the inflamed triceps tendon to heal:
1. Activity Modification
The first step is to avoid aggravating activities that overload the injured elbow tendon like pressing, pushing, weight training, or throwing. Use the injured arm lightly or wear an elbow brace to restrict motion until pain and inflammation resolve.
2. NSAID Medications
Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) or naproxen can ease inflammation and pain. Your doctor may prescribe stronger NSAID pills for more severe elbow pain and swelling.
3. Apply Ice Packs
Icing the sore triceps tendon for 15- 20 minutes several times per day helps control pain and inflammation. Use an ice pack, bag of frozen peas, or crushed ice wrapped in a damp towel.
4. Elbow Brace
Wearing an elbow brace can protect the irritated tendon from further strain until healed by restricting extension. A tennis elbow brace or strap just below the sore spot can help minimize pain with activity.
5. Physical Therapy
Once initial pain settles, physical therapy can help rehab the elbow. Gentle triceps stretching, therapeutic ultrasound, and elbow mobilization help calm inflammation while massage and exercises boost blood flow to aid healing.
The therapist will also evaluate posture and shoulder/elbow muscle balance. They can provide tips to correct any imbalance contributing to elbow strain.
Later, light strengthening builds up tendon durability and tolerance to repetitive elbow use. The key is gradually progressing elbow activity under guidance to prevent re-injury during the healing process.

Medical Treatments for Stubborn Cases
If triceps inflammation and damage do not resolve with several weeks of conservative treatment, a doctor may recommend:
- Steroid injections contain anti-inflammatory corticosteroid medication injected directly into the sore triceps tendon sheath. Steroids powerfully ease pain and swelling. However, side effects include weakened tendon tissue and thinning skin.
- Tenex procedure uses ultrasound guidance to wash out calcium deposits or scar tissue irritating the tendon. Saline is injected to separate the deposits from tendon so they can dissolve.
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections contain concentrated growth factors in blood plasma that may help tendons heal. PRP is injected into the damaged elbow tendon to stimulate healing and tissue regeneration.
- Shock wave therapy uses focused sound waves to trigger healing responses in chronically painful tendons. Multiple shock wave treatment sessions may be needed.
If conservative treatments fail and the arm lacks normal triceps function, surgery may be required to debride (remove) damaged tissue causing pain or to reattach a completely torn tendon.
Tips for Preventing Triceps Tendonitis
Here are some proactive measures to help prevent triceps tendonitis:
- Warm up shoulders and elbows thoroughly before any activity demanding forceful triceps use
- Stretch triceps muscles regularly using proper technique
- Strengthen shoulder and elbow muscles through their full range of motion to improve flexibility and stability
- Use good form and safe elbow alignment during exercises like dips, bench presses, pushdowns
- Gradually increase training intensity, weight, or repetitions to condition tendons
- Take regular rest breaks during repetitive tasks requiring elbow extension
- Use an elbow brace during activities that aggravate elbows like tennis or weightlifting
- Ice elbows after strenuous workouts or activity sessions
- Stop any activity causing elbow pain until it resolves fully
- See a doctor if you experience recurrent elbow pain that persists beyond a few days

By recognizing early warning signs of triceps tendonitis and taking proactive precautions, you can reduce risk and help keep your elbows pain-free.
When Can I Return to Activities After Triceps Tendonitis?
Your doctor will assess progress weekly and provide guidance on safely returning to sports, exercise, or repetitive tasks after elbow injury. Pain and swelling must resolve first. Resuming activities too soon frequently re-strains healing tissues.
Expect healing to take at least 6-12 weeks for minor irritation and small partial tears. Extensive tendon damage and large tears may require 3-6 months before the tendon can handle powerful contractions during sports involving elbow extension.
With minor cases, you may return to light activity after 2-3 weeks if swelling resolves and you regain full pain-free elbow motion. From there, gradually increase demands on the elbow daily as tolerated without pain.
Stop immediately and see your doctor if symptoms recur once you resume activity. This may indicate the injury requires more healing time or further treatment before attempting to return to sports or repetitive elbow use.
Adhering to recovery milestones helps prevent reinjury.

When to See an Elbow Specialist
It’s a good idea to see an orthopedic doctor who specializes in elbow injuries and sports medicine if you have:
- Ongoing pain lasting over 6 weeks despite treatment
- Inability to fully straighten the elbow after 3 months
- Repeated flares of elbow swelling and pain with activity
- Significant weakness in the injured arm
A specialist can provide focused treatments and rehab methods to help resolve stubborn cases of triceps tendonitis.
For extensive tendon damage causing persistent impairment, they may advise advanced surgical reconstruction to repair the tendon.
Can Triceps Tendonitis Come Back?
It’s possible to experience recurring bouts of triceps tendonitis, especially if you overuse the triceps before fully recovering from a prior episode. Other risk factors for recurrence include:
- Inadequate rehabilitation time before resuming sports/activities
- Poor training technique that strains the healing tendon
- Muscle strength imbalances around shoulders and elbows
- Insufficient flexibility through elbow joints and tendons
- Arthritis developing in the elbow joint
Doing proper strength training for elbows, warming up adequately before working out, using safe biomechanics during exercise, icing after activity, and avoiding overuse of healing elbows can help prevent recurrence.
See an orthopedist if elbow pain flares up repeatedly to identify and address any underlying contributors. Surgery may be warranted to remove damaged tissue irritating the tendon or release scar tissue constricting smooth gliding motion.
Key Takeaways on Triceps Tendonitis
- Triceps tendonitis causes pain where the triceps muscle tendon attaches near the elbow from sports overuse or repetitive strain.
- Typical symptoms include elbow pain when straightening the arm, swelling, stiffness, and tenderness near the back of the elbow.
- See a doctor for persistent, severe, or worsening pain over 2 weeks to assess for potential tears requiring prompt treatment.
- Anti-inflammatory medication, bracing, stretching, ice, and activity modification help calm inflammation so the elbow can heal.
- With elbow tendonitis, gradually progress rehabilitation under guidance to avoid reinjury and allow the tendon to fully heal before returning to sports or repetitive tasks.
- Proper strength training, flexibility, technique, stretching, and activity pacing helps prevent recurrent elbow flares.
In summary, overuse triceps tendonitis causes isolated pain at the back of the elbow near where the tendon inserts.
Getting an accurate diagnosis and following doctor recommendations for rest, anti-inflammatory measures, and physical therapy allows most cases to heal fully within 12 weeks.
Seek prompt attention for severe elbow injuries to avoid lasting damage impacting arm function.
Frequently Asked Questions About Triceps Tendonitis
What are the treatment options for triceps tendonitis?
Treatment options for triceps tendonitis include activity modification, icing the area, over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medication, elbow bracing, physical therapy exercises, and sometimes steroid injections or shockwave therapy for more stubborn cases. Most cases resolve within 6-12 weeks with conservative treatment.
What is tricep tendonitis?
Tricep tendonitis, also called triceps tendinitis, is inflammation of the tendon that attaches the triceps muscle of the upper arm to the elbow. This condition causes pain, stiffness, and weakness in straightening the elbow.
What is the tricep muscle and tendon?
The tricep is the large three-headed muscle on the back of the upper arm. It straightens the arm at the elbow when contracted. The triceps tendon attaches this muscle to the elbow so you can extend your arm.
What does tendinitis mean?
Tendinitis refers to inflammation and irritation of a tendon, usually from overuse or repetitive strain. In triceps tendinitis, microscopic tears in the tendon cause pain and weakness.
What is triceps tendinitis?
Triceps tendinitis is simply another term for triceps tendonitis. They both refer to inflammation of the triceps tendon at the back of the elbow joint.
What causes triceps tendonitis?
Common causes of triceps tendonitis include sports requiring repetitive arm motions like throwing or weightlifting, sudden trauma from a fall onto an outstretched hand, bone spurs rubbing the tendon, improper training, and weakness in shoulder stabilizer muscles.
How do you know if a triceps tendon is torn?
Signs of a torn triceps tendon include sudden severe pain in the back of the elbow, an immediate inability or weakness in straightening the elbow, swelling and bruising, and a visible depression above the elbow where the tendon detached. Prompt surgical repair is needed for full triceps tendon tears.
Triceps Tendonitis Summary
Triceps Tendonitis Treatment
Treatment options for triceps tendonitis focus first on resting the elbow and icing to reduce inflammation.
Anti-inflammatory medication like ibuprofen can help with pain and swelling.
Using an elbow brace and starting gentle stretching and strengthening exercises in physical therapy are also helpful.
For severe or chronic cases, a doctor may inject steroid medication or use shockwave therapy on the injured tendon to promote healing.
Most cases resolve with conservative treatment over 6-12 weeks.
Causes of Triceps Tendonitis
Common causes leading to inflammation of the triceps tendon at the back of the elbow include sports requiring repetitive elbow motions like throwing, sudden trauma from an injury or fall onto an outstretched hand, improper strength training technique and progression, bone spurs in the elbow rubbing the tendon, and shoulder muscle weakness.
Risk increases if people rapidly overload triceps activity.
Torn Triceps Tendon
A completely ruptured triceps tendon causes sudden severe pain at the back of the elbow and an inability to properly straighten the arm. Signs of a full-thickness tear include swelling, bruising, weakness extending the elbow, and a visibly depressed area above the elbow bone. This injury requires prompt surgical reattachment for the ability to regain full triceps muscle function.
In summary, this comprehensive guide covers triceps tendonitis causes like repetitive overuse and trauma, symptoms such as pain and swelling, diagnosis methods, treatment options from icing and anti-inflammatory medication to surgery for severe tears, prevention tips, and what to expect recovering to full activity after this elbow injury.
References
Cohen, M.S., Romeo, A.A. (2021). Triceps Tendon Injuries. Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 29(6), pages 293-302. https://doi.org/10.5435/JAAOS-D-19-00754
This 2021 journal article published in the Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons systematically reviews evaluation, imaging, classification systems, non-operative treatment, and surgical treatment of triceps tendon injuries including tendonitis. As a peer-reviewed medical journal, it adds significant authority and trustworthiness.
Levy, M., Goldberg, I., Meir, I. (2016). Triceps Tendon Rupture. Phys Sportsmed, 44(4), pages 420–424. https://doi.org/10.1080/00913847.2016.1254020
This review article from the authoritative Physician and Sportsmedicine journal discusses complete ruptures of the triceps tendon. Published by informa healthcare, it is a reputable medical resource that analyzes diagnosis, surgical repair techniques, rehabilitation protocols and expected outcomes based on published studies.
Sollender, J.L., Rayan, G.M., Barden, G.A. (2015). Triceps Tendon Injuries: An Anatomic, Biomechanical, and Clinical Review. Journal of Hand Surgery, 40(7), pages 1415-1419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhsa.2015.03.028
This 2015 research review from the highly regarded Journal of Hand Surgery examines the relevant anatomy, biomechanics, evaluation, and management of both partial and full triceps tendon injuries. It covers conservative treatment, surgical techniques, rehabilitation, and clinical outcomes.
For More Training Advice + Diet and Lifestyle visit us RIPL Fitness
PS: Make sure you check out the rest of our Tricep Training Guides:
12 Best Long Head Tricep Exercises
Top 17 Tricep Extension Exercises
Perfecting the Triceps Pushdown
10 Best Medial Head Tricep Exercises
10 Best Lateral Head Tricep Exercises
The Best Triceps Stretches to Loosen and Improve Flexibility

